If your phone’s LTE data suddenly stops working, you’re not alone. As carriers phase out 3G networks and rely on LTE for both voice and data services, brief outages, handoff issues, and misconfigured settings can leave even flagship phones disconnected. Industry analyses by GSMA and Opensignal indicate that LTE still carries the majority of mobile traffic worldwide—often exceeding 60% in many regions—so disruptions in LTE instantly impact everyday connectivity.
The good news is that most LTE failures stem from temporary registration glitches, network mode conflicts, or provisioning problems that you can fix within minutes. Here’s how to get back online quickly, along with the deeper checks experts perform before suggesting a call to your carrier.
Start with Quick Resets to Restore LTE
Begin by toggling airplane mode on for 10 to 20 seconds, then turn it off. This forces your phone’s modem to drop any stale connections and re-register with the tower, effectively rebooting the cellular connection. It’s like unplugging and plugging back in a cable—a simple fix that resolves many LTE stalls.
If that doesn’t work, reboot your phone completely. Restarting clears cached radio data and resets carrier settings. After rebooting, test connectivity by opening multiple apps or websites rather than relying solely on a speed test to confirm LTE is working.
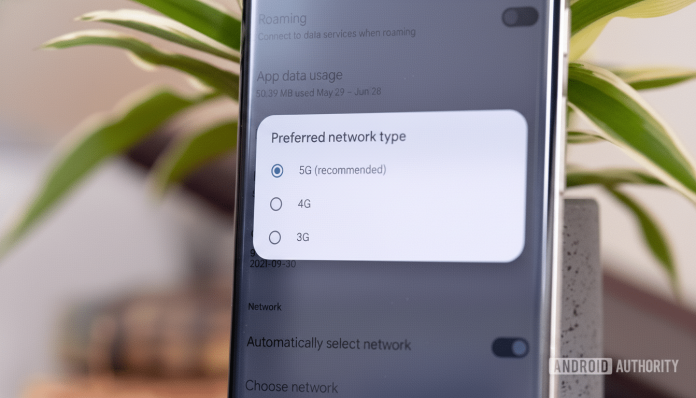
Check Network Modes and Bands for LTE Stability
Make sure your device is set to support LTE. On Android, navigate to Settings > Network or Mobile Network and select an option like 5G/4G/3G Auto. On iPhone, go to Settings > Cellular > Cellular Data Options > Voice & Data and verify LTE is enabled.
If 5G signals are unstable, disable 5G temporarily to force a solid LTE connection. Opensignal data reveals some 5G-to-LTE handovers can cause erratic performance; switching to LTE often restores consistent reliability.
Examine SIM and eSIM Provisioning
Power off your phone, remove the SIM tray, clean it gently, and reseat the SIM. Dual-SIM phones usually activate LTE on just one slot at a time. For eSIM users, ask your carrier to reprovision your profile or send a new activation QR code.
Confirm VoLTE is enabled, as some carriers restrict data or voice traffic without it. On Android, look for a VoLTE or 4G Calling toggle in Mobile Network settings, and on iPhone, verify LTE is enabled for Voice & Data. Missing options may indicate incomplete carrier provisioning.
Verify Carrier and Account Status
Before deeper troubleshooting, check for carrier outages or maintenance in your area. Even with full signal bars, LTE service can go down regionally due to storms, fiber cuts, or other disruptions.
Check your plan details—exceeding a data cap or hotspot limits can lead to throttling or temporary service blocks. MVNO customers might experience deprioritization in congested networks, which can look like LTE failure. Contact your carrier’s support to refresh your line, restore data, or confirm APN settings.
Review Phone Settings That Impact LTE
Settings such as Data Saver, Low Data Mode, or per-app restrictions can silently block LTE background data. On Android, ensure Data Saver is off or whitelist your essential apps. On iPhone, disable Low Data Mode under Cellular Data Options.
VPNs and Private DNS configurations may also disrupt LTE connectivity during outages. Temporarily disable VPNs and set DNS to automatic. If traveling, enable Data Roaming and set Network Selection to automatic so your phone can join partner networks seamlessly.
Reset Network Settings as a Last Resort
Resetting network settings often resolves tricky LTE issues after updates or SIM changes. On Android, go to Settings > System > Reset Options > Reset Wi-Fi, mobile, and Bluetooth. On iPhone, navigate to Settings > General > Transfer or Reset > Reset > Reset Network Settings. Note that you will need to re-enter saved Wi-Fi and Bluetooth pairings, but LTE usually returns after a restart.
When Hardware or Coverage Is the Culprit
Physical damage or water exposure can break antennas or modems, causing persistent poor LTE signals. Test with another SIM or phone on the same network in the same location to isolate the issue. If your device is the outlier, consider diagnostics or warranty claims.
Indoor coverage can also cause problems, as mid and high-band LTE signals often struggle to penetrate walls and metal. Try Wi-Fi calling, move closer to windows, or test LTE outside. If LTE improves, explore permanent Wi-Fi calling or carrier signal boosters.
If none of these steps restore LTE service, contact your carrier for assistance with provisioning, IMS registration, APN settings, or reprovisioning your SIM or eSIM. Most LTE issues boil down to these manageable fixes once the correct settings are adjusted.